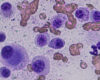
Can a single blood sample simplify the invasive and expensive work-up of tumour patients? This is a question frequently faced by both owners and veterinarians.
At the Laboklin expert panels, renowned experts provide answers to questions on exciting and current topics. We have summarised the highlights from the panel on CKD for you.
Feline coronaviruses (FCoV) are distributed worldwide and commonly seen in veterinary practice.
Small mammals are fleeing and prey animals. Serious illnesses must remain unrecognised for a long time, otherwise the animals can easily become victims of predators!
Rodenticides (‘rat poisons’) are repeatedly the cause of life-threatening poisoning in dogs and cats.
The gold standard in the diagnosis of mast cell tumours (MCT) is cytology and histopathology. Clinical staging is based on the clinical picture including the lymph node status (cytological/ histological).
Infections with Echinococcus are some of the most important zoonoses caused by cestodes.
Is the animal neutered or not? This question always arises when stray or shelter animals with missing neutering scars and unclear neutering status are presented or older, supposedly neutered animals start showing typical sexual behaviour such as mounting, barking, chasing and increased aggression.
The most important lungworm species belong to the helminth superfamily Metastrongyloidea, the adults of which live in the lungs of their vertebrate hosts.
The Laboklin expert "Round Tables" have become a well-known event, whereby invited experts engage in a moderated in-depth discussion with questions from the audience.
2023
Clinical consensus statements and guidelines are recognised medical statements and guidelines issued by a committee of experts.
Poisonings in dogs and cats are a common occurrence in veterinary practice – whether it is an emergency due to the animal ingesting potentially toxic substances or an unlikely but possible differential diagnosis.
Dermatophytes are ubiquitous, keratinophilic, filamentous fungi that infect skin, hair, and claws. They are a serious concern due to their zoonotic potential (de Matos and Kalivoda 2013).
Parasites have developed different survival strategies.
Digestive disorders are a frequent reason that pets are presented to veterinary practices, with the main complaints being, vomiting, anorexia, flatulence, weight loss and diarrhoea.
Coronaviruses have been an important topic in veterinary medicine for a long time due to their worldwide distribution and susceptibility of a wide variety of species.
The gastrointestinal microbiota is a complex community of microorganisms that colonise the digestive tract and play an important role in animal health and well-being.
Feline patients with respiratory infections are common in companion animal practice.
The senses of hearing and balance are located in the ear.
“The last child has fur” – this common social belief means that dogs often live very closely with people, like members of the family.
Chronic enteropathy – a complex topic which raises many questions.
Until recently, feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) was a fatal disease that could only be detected by pathology.
2022
When to suspect hemolysis? We suspect hemolysis especially in regenerative anemia when blood loss has been excluded...
As with all skin problems, a thorough history is the most critical tool to arrive at a diagnosis in the cat.
Turtles and tortoises are popular pets which can become very old when kept properly.
Parvoviruses play a significant role as infectious agents in various species.
Feline asthma belongs to the feline atopic syndrome (FAS), including other allergic diseases such as feline atopic skin syndrome (FASS)
Acute-phase proteins (APP) are an important component of the body’s own innate immune system.
The parameters we use to assess kidney function are so-called biomarkers.
In dogs and cats, increased urinary protein excretion is pathological and highly correlated with reduced survival of the respective animal.
Small pets are now among the most popular domestic animals in Germany (5 million small pets in 5% of all households...
How would we diagnose without laboratory tests? Whether it is blood count, pathogen detection or pathology...
2021
Approximately 1 – 3% (1) or 5 – 12% (2, 3) of cats infected with feline enteric coronavirus (FECV) develop feline infectious peritonitis (FIP).
Proliferative lesions of the oral cavity are regularly seen in both dogs and cats.
In recent years, our understanding of infectious diseases in reptiles has grown immensely.
Dogs with otitis externa (O. e.) are frequently presented to the small animal practice. Clinical signs are head shaking, scratching, restlessness and an unpleasant odour.
Diagnosing infectious diseases in rabbits is not always easy. For one thing, rabbits show clinical signs rather late and for another, there is often a time delay before they are presented to the veterinarian.
Pet reptiles are frequently presented to the practice for various types of skin lesions.
As the largest organ of the body, the skin is easily accessible for various examinations, yet the diagnostic work-up of dermatology patients can be extremely frustrating.
In Europe, cowpox virus is the most relevant representative of the genus Orthopoxvirus in the family Poxviridae.
In dogs, tumours mostly occur at the age of 9 – 12 years.
Human coeliac disease is a gluten-induced enteropathy characterised by a specific genetic genotype (HLA-DQ2/HLA-DQ8 genes) ...
Basically, the following options are available for the treatment of hyperadrenocorticism in dogs:
2020
Sodium is the most important cation in the extracellular fluid. Hence, it is essential for maintaining osmolality or the distribution of water between the extracellular space (ECS) and the intracellular space (ICS).
98% of the calcium (Ca) is contained in the bones and ensures their stability. In addition, it is also important for blood coagulation and muscle contraction.
Diarrhoeal diseases are a common problem in small mammals. As in other animal species, too, diarrhoea is characterised by defaecation with higher water content and/or increased frequency.
Patients who display unwanted behaviour are normally only presented to the practice late in their history of suffering, since behaviour is usually not associated with an illness, but solely with the animal’s circumstances and its nature.
In Germany, vector-borne infections are becoming more important in dogs and cats for the following reasons ...
Infections with the various causative agents of feline upper respiratory disease complex occur regularly despite available vaccines.
The body of mammals is colonised with countless microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa and viruses.
2019
For sick guinea pigs, laboratory diagnostics remain an important part of the diagnostic workup.
In dogs, both transitional cell carcinoma (TCC, Fig. 1) and prostate carcinoma (PCa) are highly malignant neoplasms (GRIFFIN et al. 2018).
In laboratory diagnostics, there are various parameters available for assessing the renal function that provide a good representation of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
The new version of the German Veterinary Pharmacy Act (TÄHAV), which has been in force since 1st March 2018, has raised some questions regarding the treatment of (kerato) conjunctivitis.
2018
An increasing number of dog and cat owners are looking for alternatives to commercial pet foods to feed their animals.
There are many methods available for the detection of infectious diseases in animals.
Three blood groups are regularly described in cats. The AB blood group system is comparable to the ABO system used in humans.
A leukocytosis is defined as an increase in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes) in the blood.
Dental disease and inappropriate feeding are common causes of diarrhoea. Parasites, in contrast, play a smaller role in pets.
2017
Cortisol, which is produced in the adrenal glands, is absolutely essential in physiological concentrations.
With the change in relationships from working dogs to companion dogs and cats, the expectation of owners to keep these companions for as long and as healthy as possible has increased.
2016
The pancreas is a very important digestive organ in dogs and cats and consists of an exocrine and endocrine portion.
Microscopic examination of tissue sections following formalin fixation (10%) and embedding in paraffin is used to diagnose many different lesions including tumours, lesions in organs or in the skin, or inflammation and infection.
2015
Histopathological examinations of biopsies are an important tool for diagnosing gastrointestinal disease in dogs and cats.
The abbreviation FACS stands for fluorescence activated cell sorting.
The two most important retrovirus infections found in cats, FIV and FeLV, are encountered daily in practice and in the laboratory.
2014
Enlarged toes are often painful and cause lameness. They are often difficult or impossible to treat using antibiotics.
Leukaemia is a neoplastic proliferation usually of one leukocyte population in the bone marrow.
An ACTH stimulation test is considered the gold standard for the diagnosis of Morbus Addison and therapy control of Cushing’s disease patients on Vetoryl® (active component: Trilostane).
2013
The pancreas fulfils multiple vital metabolic functions.
Ferrets (Mustella putorius furo) have only been held as pets for the last 30 years, but they are gaining in popularity.
As the liver plays a major role in an array of metabolic processes, liver diseases are connected with various clinical findings and clinicopathologic abnormalities.
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease found worldwide. Leptospira is a gram-negative, helical shaped bacterium from the group spirochetes.
Feline Upper Respiratory Infections (URI) is a collective term for infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract and the mucous membranes of cats.
Cryptosporidium are very small, obligate intracellular protozoans belonging to the Coccidia.
2012
The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is a glycoprotein that plays an important role in the sex differentiation during embryogenesis.
Over the last few decades the popularity of reptiles as pets has increased.
The very common airway disease, known as “Infectious Canine Laryngo-tracheitis” or „Kennel Cough“ is characterized by acute onset of an extreme rough, sometimes convulsive cough.
Lesions in the oral cavity are seen quite frequent in both dogs and cats. From a clinical point of view it is of great importance to know if the lesions are caused by an infection or neoplasia.
Glucocorticoids are used commonly in many different areas of veterinary medicine.